|
Expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three-Runway System |


Contents
Abbreviations
|
3RS |
Three-Runway System |
|
AAHK |
Airport Authority Hong Kong |
|
AECOM |
AECOM Asia Company Limited |
|
AFCD |
Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department |
|
AIS |
Automatic Information System |
|
ANI |
Encounter Rate of Number of Dolphins |
|
APM |
Automated People Mover |
|
AW |
Airport West |
|
BHS |
Baggage Handling System |
|
C&D |
Construction and Demolition |
|
CAP |
Contamination Assessment Plan |
|
CAR |
Contamination Assessment Report |
|
CTCC |
Construction Traffic Control Centre |
|
CWD |
Chinese White Dolphin |
|
DCM |
Deep Cement Mixing |
|
DEZ |
Dolphin Exclusion Zone |
|
DO |
Dissolved Oxygen |
|
EIA |
Environmental Impact Assessment |
|
EM&A |
Environmental Monitoring & Audit |
|
EP |
Environmental Permit |
|
EPD |
Environmental Protection Department |
|
EPSS |
Emergency Power Supply Systems |
|
ET |
Environmental Team |
|
FCZ |
Fish Culture Zone |
|
HKBCF |
Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge Hong Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities |
|
HKIA |
Hong Kong International Airport |
|
HOKLAS |
Hong Kong Laboratory Accreditation Scheme |
|
HSF |
High Speed Ferry |
|
HVS |
High Volume Sampler |
|
IEC |
Independent Environmental Checker |
|
LKC |
Lung Kwu Chau |
|
MMHK |
Mott MacDonald Hong Kong Limited |
|
MMWP |
Marine Mammal Watching Plan |
|
MSS |
Maritime Surveillance System |
|
MTRMP-CAV |
Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for Construction and Associated Vessel |
|
NEL |
Northeast Lantau |
|
NWL |
Northwest Lantau |
|
PAM |
Passive Acoustic Monitoring |
|
PM |
Project Manager |
|
SC |
Sha Chau |
|
SCLKCMP |
Sha Chau and Lung Kwu Chau Marine Park |
|
SS |
Suspended Solids |
|
SSSI |
Site of Special Scientific Interest |
|
STG |
Encounter Rate of Number of Dolphin Sightings |
|
SWL |
Southwest Lantau |
|
T2 |
Terminal 2 |
|
The Project |
The Expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three-Runway System |
|
The SkyPier Plan |
Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for High Speed Ferries of SkyPier |
|
The Manual |
The Updated EM&A Manual |
|
TSP |
Total Suspended Particulates |
|
WL |
West Lantau |
|
WMP |
Waste Management Plan |
The “Expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three-Runway System” (the Project) serves to meet the future air traffic demands at Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA). On 7 November 2014, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report (Register No.: AEIAR-185/2014) for the Project was approved and an Environmental Permit (EP) (Permit No.: EP-489/2014) was issued for the construction and operation of the Project.
Airport Authority Hong Kong (AAHK) commissioned Mott MacDonald Hong Kong Limited (MMHK) to undertake the role of Environmental Team (ET) for carrying out the Environmental Monitoring & Audit (EM&A) works during the construction phase of the Project in accordance with the Updated EM&A Manual (the Manual).
This is the 65th Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report for the Project which summarises the monitoring results and audit findings of the EM&A programme during the reporting period from 1 to 31 May 2021.
Key Activities in the Reporting Period
The key activities of the Project carried out in the reporting period included reclamation works and land-based works. Works in the reclamation areas included deep cement mixing (DCM) works, marine filling, seawall and facilities construction, together with runway and associated works. Land-based works on existing airport island involved mainly airfield works, foundation and substructure work for Terminal 2 expansion, modification and tunnel work for Automated People Mover (APM) and Baggage Handling System (BHS), and preparation work for utilities, with activities include site establishment, site office construction, road and drainage works, cable ducting, demolition, piling, and excavation works.
EM&A Activities Conducted in the Reporting Period
The monthly EM&A programme was undertaken in accordance with the Manual of the Project. Summary of the monitoring activities during this reporting period is presented as below:
|
Monitoring Activities |
Number of Sessions |
|
1-hour Total Suspended Particulates (TSP) air quality monitoring |
30 |
|
Noise monitoring |
16 |
|
Water quality monitoring |
13 |
|
Vessel line-transect surveys for Chinese White Dolphin (CWD) monitoring |
2 |
|
Land-based theodolite tracking survey effort for CWD monitoring |
2 |
Environmental auditing works, including weekly site inspections of construction works conducted by the ET and bi-weekly site inspections conducted by the Independent Environmental Checker (IEC), audit of SkyPier High Speed Ferries (HSF), audit of construction and associated vessels, and audit of implementation of Marine Mammal Watching Plan (MMWP) and Dolphin Exclusion Zone (DEZ) Plan, were conducted in the reporting period. Based on information including ET’s observations, records of Maritime Surveillance System (MSS), and contractors’ site records, it is noted that environmental pollution control and mitigation measures were properly implemented and construction activities of the Project in the reporting period did not introduce adverse impacts to the sensitive receivers.
Snapshots of EM&A Activities in the Reporting Period
|
|
|
|
|
Impact Water Quality Monitoring conducted by ET |
On-site Checking of WetSep Maintenance Record |
Inspection of the Control Room of Asphalt Plant |
Results of Impact Monitoring
The monitoring works for construction dust, construction noise, water quality, construction waste, landscape & visual, and CWD were conducted during the reporting period in accordance with the Manual.
Monitoring results of construction dust, construction waste, and CWD did not trigger the corresponding Action and Limit Levels in the reporting period.
One monitoring result of construction noise exceeded the relevant Limit Level, and the corresponding investigation was conducted as stipulated in the EM&A programme. The investigation findings concluded that the exceedance was not due to the Project.
The water quality monitoring results for all parameters, except suspended solids (SS), obtained during the reporting period were within the corresponding Action and Limit Levels stipulated in the EM&A programme. Relevant investigation and follow-up actions will be conducted according to the EM&A programme if the corresponding Action and Limit Levels are triggered. For SS, one of the testing results triggered the relevant Action Level, and the corresponding investigation was conducted accordingly. The investigation findings concluded that the case was not related to the Project. To conclude, the construction activities in the reporting period did not introduce adverse impact to all water quality sensitive receivers.
Summary of Upcoming Key Issues
Reclamation Works:
Contract 3206 Main Reclamation Works
● DCM works;
● Land-based ground improvement works;
● Seawall construction;
● Marine filling; and
● Sorting and reuse of inert waste from other 3RS contracts.
Airfield Works:
Contract 3301 North Runway Crossover Taxiway
● Cable ducting works; and
● Paving works.
Contract 3302 Eastern Vehicular Tunnel Advance Works
● Cable laying and ducting works;
● Backfilling and reinstatement works; and
● Piling and structure works.
Contract 3303 Third Runway and Associated Works
● Land-based ground improvement works;
● Operation of asphalt plant;
● Footing and utilities work; and
● Cable laying and ducting works.
Contract 3305 Airfield Ground Lighting System
● Genset installation; and
● Site establishment.
Contract 3307 Fire Training Facility
● Architectural, Builder's and Finishing works;
● Drainage and utilities works; and
● Building construction.
Third Runway Concourse:
Contract 3403 New Integrated Airport Centres Building and Civil Works
● Architectural, Builder's Work and Finishing works;
● Underground utilities construction;
● Footing construction; and
● Pre-boring and sheetpiling works.
Contract 3405 Third Runway Concourse Foundation and Substructure Works
● Foundation works;
● Piling work;
● Excavation and backfilling; and
● Road formation.
Terminal 2 Expansion:
Contract 3503 Terminal 2 Foundation and Substructure Works
● T2 re-configuration;
● Excavation works;
● Utilities road work; and
● Piling and structure works.
Contract 3508 Terminal 2 Expansion Works
● Excavation and footing construction;
● Site formation;
● Piling work; and
● Builders’ works.
Automated People Mover (APM) and Baggage Handling System (BHS):
Contract 3601 New Automated People Mover System (TRC Line)
● Rebar fixing;
● Formwork erection and removal;
● Guidebeam installation; and
● Concreting work.
Contract 3602 Existing APM System Modification Works
● Car modification; and
● Concreting work.
Construction Support (Facilities):
Contract 3721 Construction Support Infrastructure Works
● Excavation and backfilling;
● Laying of drainage pipes and ducts; and
● Road works.
Contract 3722 Construction Support Facilities
● Foundation works;
● Erection of superstructure; and
● Site establishment.
Contract 3723 Construction Support Facilities
● Foundation works;
● Erection of superstructure; and
● Site establishment.
Airport Support Infrastructure:
Contract 3801 APM and BHS Tunnels on Existing Airport Island
● Formwork and rebar fixing;
● Construction of working platform;
● Cofferdam for shaft;
● Site clearance; and
● Demolition works.
Contract 3802 APM and BHS Tunnels and Related Works
● Construction of Airside Fire Station and marine sediment treatment plant;
● Installation of sheet pipes and dewatering well;
● Pre-drilling; and
● Ducting works.
Construction Support (Services / Licences):
Contract 3901A Concrete Batching Facility
● Plant operation; and
● Material conveyor belt construction.
Contract 3901B Concrete Batching Facility
● Plant operation; and
● Foundation works for conveyor belt.
Summary Table
The following table summarises the key findings of the EM&A programme during the reporting period:
|
Yes |
No |
Details |
Analysis / Recommendation / Remedial Actions |
|
|
Breach of Limit Level^ |
|
√ |
No breach of Limit Level was recorded. |
Nil |
|
Breach of Action Level^ |
|
√ |
No breach of Action Level was recorded. |
Nil |
|
Complaint Received |
√ |
|
In the previous reporting period, a complaint regarding alleged dusty and muddy vehicles was received on 20 April 2021. |
ET requested the relevant contractors to provide information related to the complaint. Regular site inspections were conducted in which wheel washing on vehicles prior to leaving their works area was observed. For ad hoc inspections, soil and sands on road surface in Tuen Mun Public Cargo Working Area and dusty surfaces at North Eastern Quay on 3RS reclaimed land were both observed. To follow up, the contractors are reminded to ensure the wheels of outgoing vehicles from their site area are properly washed. Haul road connected to the quay would be paved and manual wheel washing would be implemented continuously. In the long term, an enhanced wheel washing measure is planned at the quays. The case was considered closed. |
|
A complaint regarding dust issue was received on 14 May 2021. |
ET requested the relevant contractor to provide information related to the complaint. Regular site inspections and joint inspections were conducted in which sprinklers and water trucks were observed operating. ET also checked the wind speed at the Chek Lap Kok wind station and the result might suggest the presence of sudden gust. Based on the information provided by the contractor and ET’s findings, the dust generation might be caused by sudden gust. Nevertheless, the contractor was reminded to continue implementing mitigation measures on dust control. The case was considered closed. |
|||
|
Notification of any summons and status of prosecutions |
|
√ |
No notification of summons or prosecution was received. |
Nil |
|
Change that affect the EM&A |
|
√ |
There was no change to the construction works that may affect the EM&A. |
Nil |
Note:
^ Only triggering of Action or Limit Level found related to Project works is counted as Breach of Action or Limit Level.
1
Introduction
1.1
Background
On 7 November 2014, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report (Register No.: AEIAR-185/2014) for the “Expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three-Runway System” (the Project) was approved and an Environmental Permit (EP) (Permit No.: EP-489/2014) was issued for the construction and operation of the Project.
Airport Authority Hong Kong (AAHK) commissioned Mott MacDonald Hong Kong Limited (MMHK) to undertake the role of Environmental Team (ET) for carrying out the Environmental Monitoring & Audit (EM&A) works during the construction phase of the Project in accordance with the Updated EM&A Manual (the Manual) submitted under EP Condition 3.1[1]. AECOM Asia Company Limited (AECOM) was employed by AAHK as the Independent Environmental Checker (IEC) for the Project.
The Project covers the expansion of the existing airport into a three-runway system (3RS) with key project components comprising land formation of about 650 ha and all associated facilities and infrastructure including taxiways, aprons, aircraft stands, a passenger concourse, an expanded Terminal 2, all related airside and landside works and associated ancillary and supporting facilities. The submarine aviation fuel pipelines and submarine power cables also require diversion as part of the works.
Construction of the Project is to proceed in the general order of diversion of the submarine aviation fuel pipelines, diversion of the submarine power cables, land formation, and construction of infrastructure, followed by construction of superstructures.
The summary of construction works programme can be referred to Section 1.4.
1.2
Scope of this Report
This is the 65th Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report for the Project which summarises the key findings of the EM&A programme during the reporting period from 1 to 31 May 2021.
1.3
Project Organisation
The Project’s organisation structure presented in Appendix B of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.1 remained unchanged during the reporting period. Contact details of the key personnel presented in Section 1.3 of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.64 remained unchanged during the reporting period.
1.4
Summary of
Construction Works
The key activities of the Project carried out in the reporting period included reclamation works and land-based works. Works in the reclamation areas included DCM works, marine filling, seawall and facilities construction, together with runway and associated works. Land-based works on existing airport island involved mainly airfield works, foundation and substructure work for Terminal 2 expansion, modification and tunnel work for APM and BHS systems, and preparation work for utilities, with activities include site establishment, site office construction, road and drainage works, cable ducting, demolition of existing facilities, piling, and excavation works.
The locations of key construction activities are presented in Figure 1.1.
1.5
Summary of EM&A Programme Requirements
The status for all environmental aspects are presented in Table 1.1. The EM&A requirements remained unchanged during the reporting period.
Table 1.1: Summary of status for all environmental aspects under the Updated EM&A Manual
|
Parameters |
EM&A Requirements |
Status |
|
Air Quality |
||
|
Baseline Monitoring |
At least 14 consecutive days before commencement of construction work |
The baseline air quality monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
At least 3 times every 6 days |
On-going |
|
Noise |
||
|
Baseline Monitoring |
Daily for a period of at least two weeks prior to the commencement of construction works |
The baseline noise monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
Weekly |
On-going |
|
Water Quality |
||
|
General Baseline Water Quality Monitoring for reclamation, water jetting and field joint works |
Three days per week, at mid-flood and mid-ebb tides, for at least four weeks prior to the commencement of marine works. |
The baseline water quality monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
General Impact Water Quality Monitoring for reclamation, water jetting and field joint works |
Three days per week, at mid-flood and mid-ebb tides. |
On-going for reclamation works. General impact water quality monitoring for water jetting works was completed on 23 May 2017. |
|
Initial Intensive Deep Cement Mixing (DCM) Water Quality Monitoring |
At least four weeks |
The Initial Intensive DCM Monitoring Report was submitted and approved by EPD in accordance with the Detailed Plan on DCM. |
|
Regular DCM Water Quality Monitoring |
Three times per week until completion of DCM works. |
On-going |
|
Sewerage and Sewage Treatment |
||
|
Methodology for carrying out annual sewage flow monitoring for concerned gravity sewer |
Methodology to be prepared and submitted to EPD at least one year before commencement of the operation of 3RS |
The proposed methodology of the annual sewage flow monitoring was submitted to EPD. |
|
Details of the routine H2S monitoring system for the sewerage system of 3RS |
Details to be prepared and submitted to EPD at least one year before commencement of the operation of 3RS |
The details of the routine H2S monitoring system will be prepared and submitted to EPD at least one year before commencement of operation of 3RS. |
|
Waste Management |
||
|
Waste Monitoring |
At least weekly |
On-going |
|
Land Contamination |
||
|
Supplementary Contamination Assessment Plan (CAP) |
At least 3 months before commencement of any soil remediation works. |
The Supplementary CAP was submitted and approved by EPD under EP Condition 2.20. |
|
Contamination Assessment Report (CAR) for Golf Course |
CAR to be submitted for golf course |
The CAR for Golf Course was submitted and accepted by EPD. |
|
Contamination Assessment Reports (CAR) for Terminal 2 Emergency Power Supply Systems |
CAR to be submitted for Terminal 2 Emergency Power Supply Systems |
The CARs for Terminal 2 Emergency Power Supply Systems were submitted and accepted by EPD. |
|
Terrestrial Ecology |
||
|
Pre-construction Egretry Survey Plan |
Once per month in the breeding season between April and July, prior to the commencement of HDD drilling works. |
The Egretry Survey Plan was submitted and approved by EPD under EP Condition 2.14. |
|
Ecological Monitoring |
Monthly monitoring during the HDD construction works period from August to March. |
The terrestrial ecological monitoring at Sheung Sha Chau was completed in January 2019. |
|
Marine Ecology |
||
|
Pre-Construction Phase Coral Dive Survey |
Prior to marine construction works |
The Coral Translocation Plan was submitted and approved by EPD under EP Condition 2.12. |
|
Coral Translocation |
- |
The coral translocation was completed. |
|
Post-Translocation Coral Monitoring |
As per an enhanced monitoring programme based on the Coral Translocation Plan |
The post-translocation monitoring programme according to the Coral Translocation Plan was completed in April 2018. |
|
Chinese White Dolphins (CWD) |
||
|
Baseline Monitoring |
6 months of baseline surveys before the commencement of land formation related construction works. Vessel line transect surveys: Two full surveys per month; Land-based theodolite tracking surveys: Two days per month at the Sha Chau station and two days per month at the Lung Kwu Chau station; and Passive Acoustic Monitoring (PAM): For the whole duration of baseline period. |
Baseline CWD results were reported in the CWD Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD in accordance with EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
Vessel line transect surveys: Two full surveys per month; Land-based theodolite tracking surveys: One day per month at the Sha Chau station and one day per month at the Lung Kwu Chau station; and PAM: For the whole duration for land formation related construction works. |
On-going |
|
Landscape & Visual |
|
|
|
Landscape & Visual Plan |
At least 3 months before the commencement of construction works on the formed land of the Project. |
The Landscape & Visual Plan was submitted and approved by EPD under EP Condition 2.18 |
|
Baseline Monitoring |
One-off survey within the Project site boundary prior to commencement of any construction works |
The baseline landscape & visual monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
Weekly |
On-going |
|
Environmental Auditing |
|
|
|
Regular site inspection |
Weekly |
On-going |
|
Marine Mammal Watching Plan (MMWP) implementation measures |
Monitor and check |
On-going |
|
Dolphin Exclusion Zone (DEZ) Plan implementation measures |
Monitor and check |
On-going |
|
SkyPier High Speed Ferries (HSF) implementation measures |
Monitor and check |
On-going |
|
Construction and Associated Vessels Implementation measures |
Monitor and check |
On-going |
|
Silt Curtain Deployment Plan implementation measures |
Monitor and check |
On-going |
|
Spill Response Plan implementation measures |
Monitor and check |
On-going |
|
Complaint Hotline and Email channel |
Construction phase |
On-going |
|
Environmental Log Book |
Construction phase |
On-going |
Taking into account the construction works in this reporting period, impact monitoring of air quality, noise, water quality, waste management, landscape & visual, and CWD were carried out in the reporting period.
The EM&A programme also involved weekly site inspections and related auditing conducted by the ET for checking the implementation of the required environmental mitigation measures recommended in the approved EIA Report. To promote the environmental awareness and enhance the environmental performance of the contractors, environmental trainings and regular environmental management meetings were conducted during the reporting period, which are summarised as below:
● Two skipper training sessions provided by ET: 12 and 24 May 2021; and
● Seventeen environmental management meetings for EM&A review with works contracts: 6, 7, 11, 12, 17, 18, 21, 24, 26, 27 and 28 May 2021.
The EM&A programme has been following the recommendations presented in the approved EIA Report and the Manual. A summary of implementation status of the environmental mitigation measures for the construction phase of the Project during the reporting period is provided in Appendix A.
2
Air Quality Monitoring
Air quality monitoring of 1-hour Total Suspended Particulates (TSP) was conducted three times every six days at two representative monitoring stations in the vicinity of air sensitive receivers in Tung Chung and villages in North Lantau in accordance with the Manual. Table 2.1 describes the details of the monitoring stations. Figure 2.1 shows the locations of the monitoring stations.
Table 2.1: Locations of Impact Air Quality Monitoring Stations
|
Monitoring Station |
Location |
|
AR1A |
Man Tung Road Park |
|
AR2 |
Village House at Tin Sum |
2.1
Action and Limit
Levels
In accordance with the Manual, baseline air quality monitoring of 1-hour TSP levels at the two air quality monitoring stations were established as presented in the Baseline Monitoring Report. The Action and Limit Levels of the air quality monitoring stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme are provided in Table 2.2.
Table 2.2: Action and Limit Levels of Air Quality Monitoring
|
Monitoring Station |
Action Level (mg/m3) |
Limit Level (mg/m3) |
|
AR1A |
306 |
500 |
|
AR2 |
298 |
2.2
Monitoring Equipment
Portable direct reading dust meter was used to carry out the air quality monitoring. Details of equipment used in the reporting period are given in Table 2.3.
Table 2.3: Air Quality Monitoring Equipment
|
Brand and Model |
Last Calibration Date |
Calibration Certificate Provided in |
|
|
Portable direct reading dust meter (Laser dust monitor) |
SIBATA LD-3B-2 (Serial No. 296098) |
20 Oct 2020 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 58, Appendix E |
|
SIBATA LD-3B-1 (Serial No. 597337) |
10 May 2021 |
2.3
Monitoring
Methodology
2.3.1
Measuring Procedure
The measurement procedures involved in the impact air quality monitoring can be summarised as follows:
a. The portable direct reading dust meter was mounted on a tripod at a height of 1.2m above the ground.
b. Prior to the measurement, the equipment was set up for 1 minute span check and 6 second background check.
c. The one hour dust measurement was started. Site conditions and dust sources at the nearby area were recorded on a record sheet.
d. When the measurement completed, the “Count” reading per hour was recorded for result calculation.
2.3.2
Maintenance and Calibration
The portable direct reading dust meter is calibrated every year against high volume sampler (HVS) to check the validity and accuracy of the results measured by direct reading method. The calibration record of the HVS provided in Appendix D, and the calibration certificates of portable direct reading dust meters listed in Table 2.3 are valid in the reporting period.
2.4
Summary of Monitoring Results
The air quality monitoring schedule involved in the reporting period is provided in Appendix B.
The air quality monitoring results in the reporting period are summarised in Table 2.4. Detailed impact monitoring results are presented in Appendix C.
Table 2.4: Summary of Air Quality Monitoring Results
|
Monitoring Station |
1-hr TSP Concentration Range (mg/m3) |
Action Level (mg/m3) |
Limit Level (mg/m3) |
|
AR1A |
14 - 74 |
306 |
500 |
|
AR2 |
12 - 36 |
298 |
The monitoring results were within the corresponding Action and Limit Levels at all monitoring stations in the reporting period.
General meteorological conditions throughout the impact monitoring period were recorded. Wind data including wind speed and wind direction for each monitoring day were collected from the Chek Lap Kok Wind Station.
2.5
Conclusion
No dust emission source was observed at the monitoring stations during the monitoring sessions. As the sensitive receivers were far away from the construction activities, with the implementation of dust control measures, there was no adverse impact at the sensitive receivers attributable to the works of the Project.
3
Noise Monitoring
Noise monitoring in the form of 30-minute measurements of Leq, L10, and L90 levels was conducted once per week between 0700 and 1900 on normal weekdays at four representative monitoring stations in the vicinity of noise sensitive receivers in Tung Chung and villages in North Lantau in accordance with the Manual. Table 3.1 describes the details of the monitoring stations. Figure 2.1 shows the locations of the monitoring stations.
Table 3.1: Locations of Impact Noise Monitoring Stations
|
Monitoring Station |
Location |
Type of measurement |
|
NM1A |
Man Tung Road Park |
Free field |
|
NM2(1) |
Tung Chung West Development |
To be determined |
|
NM3A(2) |
Site Office |
Facade |
|
NM4 |
Ching Chung Hau Po Woon Primary School |
Free field |
|
NM5 |
Village House in Tin Sum |
Free field |
|
NM6 |
House No. 1, Sha Lo Wan |
Free field |
Note:
(1) As described in Section 4.3.3 of the Manual, noise monitoring at NM2 will only commence after occupation of the future Tung Chung West Development.
(2) According to Section 4.3.3 of the Manual, the noise monitoring at NM3A was temporarily suspended starting from 1 September 2018 and would be resumed with the completion of the Tung Chung East Development.
3.1
Action and Limit Levels
In accordance with the Manual, baseline noise levels at the noise monitoring stations were established as presented in the Baseline Monitoring Report. The Action and Limit Levels of the noise monitoring stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme are provided in Table 3.2.
Table 3.2: Action and Limit Levels for Noise Monitoring
|
Monitoring Stations |
Time Period |
Action Level |
Limit Level, Leq(30mins) dB(A) |
|
NM1A, NM2, NM3A, NM4, NM5 and NM6 |
0700-1900 hours on normal weekdays |
When one documented complaint is received from any one of the sensitive receivers |
75dB(A)(1) |
Note:
(1) The Limit Level for NM4 is reduced to 70dB(A) for being an educational institution. During school examination period, the Limit Level is further reduced to 65dB(A).
3.2
Monitoring
Equipment
Noise monitoring was performed using sound level meter at each designated monitoring station. The sound level meters deployed comply with the International Electrotechnical Commission Publications 651:1979 (Type 1) and 804:1985 (Type 1) specifications. Acoustic calibrator was used to check the sound level meters by a known sound pressure level for field measurement. Details of equipment used in the reporting period are given in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3: Noise Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
Last Calibration Date |
Calibration Certificate Provided in |
|
Integrated Sound Level Meter |
Rion NL-52 (Serial No. 00998505) |
20 Mar 2021 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 63, Appendix E |
|
Rion NL-52 (Serial No. 01287679) |
21 Jun 2020 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 54, Appendix E |
|
|
Acoustic Calibrator |
Casella CEL-120/1 (Serial No. 2383737) |
12 Sep 2020 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 57, Appendix D |
|
Castle GA607 (Serial No. 040162) |
20 Mar 2021 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 63, Appendix E |
3.3
Monitoring
Methodology
3.3.1
Monitoring Procedure
The monitoring procedures involved in the noise monitoring can be summarised as follows:
a. The sound level meter was set on a tripod at least a height of 1.2m above the ground for free-field measurements at monitoring stations NM1A, NM4, NM5 and NM6. A correction of +3dB(A) was applied to the free field measurements.
b. Façade measurements were made at the monitoring station NM3A.
c. Parameters such as frequency weighting, time weighting and measurement time were set.
d. Prior to and after each noise measurement, the meter was calibrated using the acoustic calibrator. If the difference in the calibration level before and after measurement was more than 1dB(A), the measurement would be considered invalid and repeat of noise measurement would be required after re-calibration or repair of the equipment.
e. During the monitoring period, Leq, L10 and L90 were recorded. In addition, site conditions and noise sources were recorded on a record sheet.
f. Noise measurement results, when higher than the baseline monitoring levels, were corrected with reference to the baseline monitoring levels.
g. Observations were recorded when high intrusive noise (e.g. dog barking, helicopter noise) was observed during the monitoring.
3.3.2
Maintenance and Calibration
The maintenance and calibration procedures are summarised below:
a. The microphone head of the sound level meter was cleaned with soft cloth at regular intervals.
b. The meter and calibrator were sent to the supplier or laboratory accredited under Hong Kong Laboratory Accreditation Scheme (HOKLAS) to check and calibrate at yearly intervals.
Calibration certificates of the sound level meters and acoustic calibrators used in the noise monitoring listed in Table 3.3 are valid in the reporting period.
3.4
Summary of Monitoring Results
The noise monitoring schedule involved in the reporting period is provided in Appendix B.
The noise monitoring results in the reporting period are summarised in Table 3.4. Detailed impact monitoring results are presented in Appendix C.
Table 3.4: Summary of Construction Noise Monitoring Results
|
Monitoring Station |
Noise Level Range, dB(A) Leq (30mins) |
Limit Level, dB(A) Leq (30mins) |
|
NM1A(1)(3) |
70 - 76 |
75 |
|
NM4(1) |
60 - 66 |
70(2) |
|
NM5(1)(3) |
57 - 62 |
75 |
|
NM6(1)(3) |
60 - 65 |
75 |
Notes:
(1) +3dB(A) Façade correction included;
(2) Reduced to 65dB(A) during school examination periods at NM4. School examination took place from 31 May to 4 June 2021.
(3) Some of the noise measurement results were higher than the baseline monitoring levels. In order to reduce the influence of non-Project related noise on the monitoring results, these measurement results were corrected with reference to the baseline monitoring levels.
No complaints were received from any sensitive receiver that triggered the Action Level.
One of the monitoring results triggered the corresponding Limit Level at NM1A on 28 May 2021. In accordance with Event and Action Plan stipulated in the Manual, EPD, IEC and Contractor were informed when the corresponding Limit Level was triggered.
It was confirmed from the on-site observation by monitoring team during the whole period of monitoring that the major noise source was from cicadas chirping. Moreover, no major construction noise was observed during the whole monitoring period. As confirmed with the contractors, noise mitigation measures were implemented for their construction works during the monitoring period.
Therefore, the case was considered not due to Project activities. The mitigation measures that have been implemented were considered effective and will be implemented continuously.
3.5
Conclusion
During the reporting period, it is noted that the vast majority of monitoring results were within their corresponding Action and Limit Levels, while only one result triggered the corresponding Limit Level, and investigation was conducted accordingly.
Based on the investigation findings, the result that triggered the corresponding Limit Level was not due to the Project. Therefore, the Project did not cause adverse impact at the noise sensitive receivers. All required actions under the Event and Action Plan were followed. This case appeared to be due to other sources not related to the Project.
As the construction activities were far away from the monitoring stations, major sources of noise dominating the monitoring stations observed during the construction noise impact monitoring were cicadas chirping and traffic noise near NM1A, school activities at NM4 and aircraft noise near NM5 and NM6 during this reporting period. It is considered that the monitoring work during the reporting period was effective and there was no adverse impact attributable to the Project activities.
4
Water Quality Monitoring
Water quality monitoring of DO, pH, temperature, salinity, turbidity, suspended solids (SS), total alkalinity, chromium, and nickel was conducted three days per week, at mid-ebb and mid-flood tides, at a total of 23 water quality monitoring stations, comprising 12 impact (IM) stations, 8 sensitive receiver (SR) stations and 3 control (C) stations in the vicinity of water quality sensitive receivers around the airport island in accordance with the Manual. The purpose of water quality monitoring at the IM stations is to promptly capture any potential water quality impact from the Project before it could become apparent at sensitive receivers (represented by the SR stations). Table 4.1 describes the details of the monitoring stations. Figure 4.1 shows the locations of the monitoring stations.
Table 4.1: Monitoring Locations and Parameters of Impact Water Quality Monitoring
|
Monitoring Station |
Description |
Coordinates |
Parameters |
|
|
|
|
Easting |
Northing |
|
|
C1 |
Control Station |
804247 |
815620 |
General Parameters DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS
DCM Parameters Total Alkalinity, Heavy Metals(2) |
|
C2 |
Control Station |
806945 |
825682 |
|
|
C3(3) |
Control Station |
817803 |
822109 |
|
|
IM1 |
Impact Station |
807132 |
817949 |
|
|
IM2 |
Impact Station |
806166 |
818163 |
|
|
IM3 |
Impact Station |
805594 |
818784 |
|
|
IM4 |
Impact Station |
804607 |
819725 |
|
|
IM5 |
Impact Station |
804867 |
820735 |
|
|
IM6 |
Impact Station |
805828 |
821060 |
|
|
IM7 |
Impact Station |
806835 |
821349 |
|
|
IM8 |
Impact Station |
808140 |
821830 |
|
|
IM9 |
Impact Station |
808811 |
822094 |
|
|
IM10 |
Impact Station |
809794 |
822385 |
|
|
IM11 |
Impact Station |
811460 |
822057 |
|
|
IM12 |
Impact Station |
812046 |
821459 |
|
|
SR1A(1) |
Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge Hong Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities (HKBCF) Seawater Intake for cooling |
812660 |
819977 |
General Parameters DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS |
|
SR2(3) |
Planned marine park / hard corals at The Brothers / Tai Mo To
|
814166 |
821463 |
General Parameters DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS
DCM Parameters Total Alkalinity, Heavy Metals(2)(4) |
|
SR3 |
Sha Chau and Lung Kwu Chau Marine Park / fishing and spawning grounds in North Lantau |
807571 |
822147 |
General Parameters DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS
General Parameters DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS
|
|
SR4A |
Sha Lo Wan |
807810 |
817189 |
|
|
SR5A |
San Tau Beach SSSI |
810696 |
816593 |
|
|
SR6A(5) |
Tai Ho Bay, Near Tai Ho Stream SSSI |
814739 |
817963 |
|
|
SR7 |
Ma Wan Fish Culture Zone (FCZ) |
823742 |
823636 |
|
|
SR8(6) |
Seawater Intake for cooling at Hong Kong International Airport (East) |
811623 |
820390 |
|
Notes:
(1) With the operation of HKBCF, water quality monitoring at SR1A station was commenced on 25 October 2018. To better reflect the water quality in the immediate vicinity of the intake, the monitoring location of SR1A has been shifted closer to the intake starting from 5 January 2019.
(2) Details of selection criteria for the two heavy metals for regular DCM monitoring refer to the Detailed Plan on Deep Cement Mixing available on the dedicated 3RS website (http://env.threerunwaysystem.com/en/ep-submissions.html). DCM specific water quality monitoring parameters (total alkalinity and heavy metals) were only conducted at C1 to C3, SR2, and IM1 to IM12.
(3) According to the Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Report, C3 station is not adequately representative as a control station of impact/ SR stations during the flood tide. The control reference has been changed from C3 to SR2 from 1 September 2016 onwards.
(4) Total alkalinity and heavy metals results are collected at SR2 as a control station for regular DCM monitoring.
(5) As the access to SR6 was obstructed by the construction activities and temporary structures for Tung Chung New Town Extension, the monitoring location has been relocated to SR6A starting from 8 August 2019.
(6) The monitoring location for SR8 is subject to further changes due to silt curtain arrangements and the progressive relocation of this seawater intake.
4.1
Action and Limit Levels
In accordance with the Manual, baseline water quality levels at the above-mentioned representative water quality monitoring stations were established as presented in the Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Report. The Action and Limit Levels of general water quality monitoring and regular DCM monitoring stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme are provided in Table 4.2. The control and impact stations during ebb tide and flood tide for general water quality monitoring and regular DCM monitoring are presented in Table 4.3.
Table 4.2: Action and Limit Levels for General Water Quality Monitoring and Regular DCM Monitoring
|
Parameters |
Action Level (AL) |
Limit Level (LL) |
|||
|
Action and Limit Levels for general water quality monitoring and regular DCM monitoring (excluding SR1A & SR8) |
|||||
|
General Water Quality Monitoring |
DO in mg/l (Surface, Middle & Bottom) |
Surface and Middle 4.5mg/l |
Surface and Middle 4.1mg/l 5mg/l for Fish Culture Zone (SR7) only |
||
|
Bottom 3.4mg/l |
Bottom 2.7mg/l |
||||
|
Suspended Solids (SS) in mg/l |
23 |
or 120% of upstream control station at the same tide of the same day, whichever is higher |
37 |
or 130% of upstream control station at the same tide of the same day, whichever is higher |
|
|
Turbidity in NTU |
22.6 |
36.1 |
|||
|
Regular DCM Monitoring |
Total Alkalinity in ppm |
95 |
99 |
||
|
Representative Heavy Metals for regular DCM monitoring (Chromium) in µg/l |
0.2 |
0.2 |
|||
|
Representative Heavy Metals for regular DCM monitoring (Nickel) in µg/l |
3.2 |
|
3.6 |
|
|
|
Action and Limit Levels SR1A |
|
|
|
||
|
SS (mg/l)) |
33 |
|
42 |
|
|
|
Action and Limit Levels SR8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SS (mg/l) |
52 |
|
60 |
|
|
Notes:
(1) For DO measurement, non-compliance occurs when monitoring result is lower than the limits.
(2) For parameters other than DO, non-compliance of water quality results when monitoring results is higher than the limits.
(3) Depth-averaged results are used unless specified otherwise.
(4) Details of selection criteria for the two heavy metals for regular DCM monitoring refer to the Detailed Plan on Deep Cement Mixing available on the dedicated 3RS website (http://env.threerunwaysystem.com/en/ep-submissions.html)
(5) The Action and Limit Levels for the two representative heavy metals chosen will be the same as that for the intensive DCM monitoring.
Table 4.3: The Control and Impact Stations during Flood Tide and Ebb Tide for General Water Quality Monitoring and Regular DCM Monitoring
|
Control Station |
Impact Stations |
|
Flood Tide |
|
|
C1 |
IM1, IM2, IM3, IM4, IM5, IM6, IM7, IM8, SR3 |
|
SR2(1) |
IM7, IM8, IM9, IM10, IM11, IM12, SR1A, SR3, SR4A, SR5A, SR6A, SR8 |
|
Ebb Tide |
|
|
C1 |
SR4A, SR5A, SR6A |
|
C2 |
IM1, IM2, IM3, IM4, IM5, IM6, IM7, IM8, IM9, IM10, IM11, IM12, SR1A, SR2, SR3, SR7, SR8 |
Note:
(1) As per findings of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Report, the control reference has been changed from C3 to SR2 from 1 September 2016 onwards.
4.2
Monitoring Equipment
Table 4.4 summarises the equipment used in the reporting period for monitoring of specific water quality parameters under the water quality monitoring programme.
Table 4.4: Water Quality Monitoring Equipment
|
Brand and Model |
Last Calibration Date |
Calibration Certificate Provided in |
|
|
Multifunctional Meter (measurement of DO, pH, temperature, salinity and turbidity) |
YSI 6920V2 (Serial No. 0001C6A7) |
22 Apr 2021 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 64, Appendix E |
|
YSI 6920V2 (Serial No. 0001CF6C) |
20 May 2021 |
||
|
YSI ProDSS (Serial No. 17H105557) |
3 Feb 2021 (1) |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 62, Appendix D |
|
|
YSI ProDSS (Serial No. 18A104824) |
25 Feb 2021 (1) |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 62, Appendix D |
|
|
YSI ProDSS (Serial No. 15M100005) |
25 Mar 2021 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 63, Appendix E |
|
|
YSI ProDSS (Serial No. 16H104234) |
22 Apr 2021 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 64, Appendix E |
|
|
YSI ProDSS (Serial No. 16H104233) |
20 May 2021 |
||
|
YSI ProDSS (Serial No. 17E100747) |
25 Mar 2021 |
Monthly EM&A Report No. 63, Appendix E |
|
|
Digital Titrator (measurement of total alkalinity) |
Titrette Bottle-top Burette, 50ml (Serial No. 10N64701) |
24 May 2021 |
|
Note:
(1) The monitoring equipment was not used in the reporting period after the expiry date of the calibration certificate.
Other equipment used as part of the impact water quality monitoring programme are listed in Table 4.5.
Table 4.5: Other Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
|
Water Sampler |
Van Dorn Water Sampler |
|
Positioning Device (measurement of GPS) |
Garmin eTrex Vista HCx |
|
Current Meter (measurement of current speed and direction, and water depth) |
Sontek HydroSurveyor |
4.3
Monitoring
Methodology
4.3.1
Measuring Procedure
Water quality monitoring samples were taken at three depths (at 1m below surface, at mid-depth, and at 1m above bottom) for locations with water depth >6m. For locations with water depth between 3m and 6m, water samples were taken at two depths (surface and bottom). For locations with water depth <3m, only the mid-depth was taken. Duplicate water samples were taken and analysed.
The water samples for all monitoring parameters were collected, stored, preserved and analysed according to the Standard Methods, APHA 22nd ed. and/or other methods as agreed by the EPD. In-situ measurements at monitoring locations including temperature, pH, DO, turbidity, salinity, alkalinity and water depth were collected by equipment listed in Table 4.4 and Table 4.5. Water samples for heavy metals and SS analysis were stored in high density polythene bottles with no preservative added, packed in ice (cooled to 4ºC without being frozen), delivered to the laboratory within 24 hours of collection.
4.3.2
Maintenance and Calibration
Calibration of In-situ Instruments
Wet bulb calibration for a DO meter was carried out before commencement of monitoring and after completion of all measurements each day. Calibration was not conducted at each monitoring location as daily calibration is adequate for the type of DO meter employed. A zero check in distilled water was performed with the turbidity probe at least once per monitoring day. The probe was then calibrated with a solution of known NTU. In addition, the turbidity probe was calibrated at least twice per month to establish the relationship between turbidity readings (in NTU) and levels of SS (in mg/l). Accuracy check of the digital titrator was performed at least once per monitoring day.
Calibration certificates of the monitoring equipment used in the reporting period are listed in Table 4.4.
4.3.3
Laboratory
Measurement / Analysis
Analysis of SS and heavy metals have been carried out by a HOKLAS accredited laboratory, ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd (Reg. No. HOKLAS 066). Sufficient water samples were collected at all the monitoring stations for carrying out the laboratory SS and heavy metals determination. The SS and heavy metals determination works were started within 24 hours after collection of the water samples. The analysis of SS and heavy metals have followed the standard methods summarised in Table 4.6. The QA/QC procedures for laboratory measurement/ analysis of SS and heavy metals were presented in Appendix F of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.8.
Table 4.6: Laboratory Measurement/ Analysis of SS and Heavy Metals
|
Parameters |
Instrumentation |
Analytical Method |
Reporting Limit |
|
SS |
Analytical Balance |
APHA 2540D |
2mg/l |
|
Heavy Metals |
|
|
|
|
Chromium (Cr) |
ICP-MS |
USEPA 6020A |
0.2µg/l |
|
Nickel (Ni) |
ICP-MS |
USEPA 6020A |
0.2µg/l |
4.4
Summary of Monitoring Results
The water quality monitoring schedule for the reporting period is updated and provided in Appendix B.
The water quality monitoring results for all parameters, except SS, obtained during the reporting period were within their corresponding Action and Limit Levels. The detailed monitoring results are presented in Appendix C.
For SS, a testing result triggered the corresponding Action Level, and investigation was conducted accordingly.
Table 4.7 presents the summary of the SS compliance status at IM and SR stations during mid-ebb for the reporting period.
Table 4.7: Summary of SS Compliance Status (Mid-Ebb Tide)
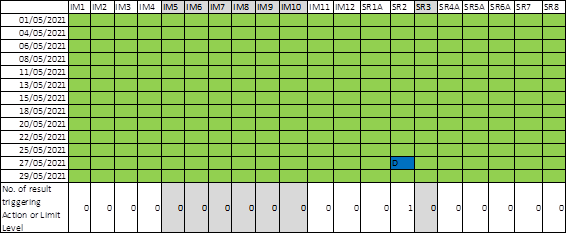
|
Note: Detailed results are presented in Appendix C. |
|
|
Legend: |
|
|
|
The monitoring results were within the corresponding Action and Limit Levels |
|
D |
Monitoring result triggered the Action Level at monitoring station located downstream of the Project based on dominant tidal flow |
|
|
Upstream station with respect to the Project during the respective tide based on dominant tidal flow |
One of the monitoring results triggered the corresponding Action Level on 27 May 2021. In accordance with Event and Action Plan stipulated in the Manual, IEC and Contractor were informed when the corresponding Action or Limit Levels were triggered.
Investigation focusing on the case which occurred at monitoring station located downstream of the Project was carried out. Details of the Project’s marine construction activities and site observations on the concerned monitoring day were collected. Findings were summarized in Table 4.8.
Table 4.8: Summary of Findings from Investigation of SS Monitoring Results
|
Date |
Marine construction works nearby |
Approximate distance from marine construction works
|
Status of water quality measures (if applicable) |
Construction vessels in the vicinity |
Turbidity / Silt plume observed near the monitoring station |
Action or Limit Level triggered due to Project |
|
27/05/2021 |
No marine construction works |
Not applicable |
Not applicable |
No |
No |
No |
For SS result recorded in ebb tide at SR2 on 27 May 2021 which triggered the corresponding Action Level, no silt plume was observed at this monitoring station and appropriate mitigation measures were implemented properly by contractors. No construction vessel was observed in the vicinity of SR2 during monitoring. It is noted that no marine construction activity was conducted for the whole project on that day and no abnormal observation was identified on the same day. Furthermore, all monitoring results recorded at IM stations, which are located closer to the Project Area, were within the Action and Limit Levels. Therefore, the case was considered unlikely due to the Project.
4.5
Conclusion
During the reporting period, it is noted that the vast majority of monitoring results were within their corresponding Action and Limit Levels, while only one result triggered the corresponding Action Level, and investigation was conducted accordingly.
Based on the investigation findings, the result that triggered the corresponding Action Level was not due to the Project. Therefore, the Project did not cause adverse impact at the water quality sensitive receivers. All required actions under the Event and Action Plan were followed. These case appeared to be due to natural fluctuation or other sources not related to the Project.
Nevertheless, as part of the EM&A programme, the construction methods and mitigation measures for water quality will continue to be monitored and opportunities for further enhancement will continue to be explored and implemented where possible, to strive for better protection of water quality and the marine environment.
In the meantime, the contractors were reminded to implement and maintain all mitigation measures during weekly site inspection and regular environmental management meetings. These include maintaining mitigation measures properly for reclamation works including DCM works, marine filling and seawall construction as recommended in the Manual.
5 Waste
Management
In accordance with the Manual, the waste generated from construction activities was audited once per week to determine if wastes are being managed in accordance with the Waste Management Plan (WMP) prepared for the Project, contract-specific WMP, and any statutory and contractual requirements. All aspects of waste management including waste generation, storage, transportation and disposal were assessed during the audits.
5.1
Action and Limit Levels
The Action and Limit Levels of the construction waste are provided in Table 5.1.
Table 5.1: Action and Limit Levels for Construction Waste
|
Monitoring Stations |
Action Level |
Limit Level |
|
Construction Area |
When one valid documented complaint is received |
Non-compliance of the WMP, contract-specific WMPs, any statutory and contractual requirements |
5.2
Waste Management Status
Weekly monitoring on all works contracts were carried out by the ET to check and monitor the implementation of proper waste management practices during the construction phase.
Recommendations made included provision and maintenance of proper chemical waste storage area, as well as handling, segregation, and regular disposal of general refuse. The contractors have taken actions to implement the recommended measures. Waste management audits were carried out by ET according to the requirement of the Waste Management Plan, Updated EM&A Manual and the implementation schedule of the waste management mitigation measures in Appendix A.
Based on updated information provided by contractors, construction waste generated in the reporting period is summarised in Table 5.2. Proactive measures have been undertaken during the re-configuration of T2 building. The contractor has established the recycling strategy for C&D materials with proper planning and design to maximize recycling and reuse. Dedicated recyclers were employed for different kinds of recyclable materials by the contractor, and ET and IEC have carried out site visit to recyclers’ faciltities to review recycling process. Recycling materials before leaving the site are weighted by a weight bridge and monitored by CCTV system. Dedicated areas for sorting of materials are established on site. Recyclable materials such as steel, reinforcement bar, structural steel, aluminum, copper, other metals and glass are sorted on-site and transported off-site for recycling. ET and IEC have carried out site audits regularly and reviewed the trip ticket system.
Table 5.2: Construction Waste Statistics
|
|
C&D(1) Material Stockpiled for Reuse or Recycle (m3) |
C&D Material Reused in the Project (m3) |
C&D Material Reused in other Projects (m3) |
C&D Material Transferred to Public Fill (m3) |
Chemical Waste (kg) |
Chemical Waste (l) |
General Refuse (tonne) |
|
|
April 2021(2)(3) |
*26,029 |
*57,644 |
*1,766 |
4,140 |
0 |
0 |
1,194 |
|
|
May 2021(2)(4) |
14,776 |
153,950 |
1,444 |
10,375 |
0 |
2,800 |
1,080 |
|
|
Notes: (1) C&D refers to Construction and Demolition. (2) Metals, paper and/or plastics were recycled in the reporting period. (3) Updated figure for the previous month is reported and marked with an asterisk (*). Updated figures for earlier months will be reported in the forthcoming Quarterly and Annual EM&A Reports. (4) The data was based on the information provided by contractors up to the submission date of this Monthly EM&A Report, and might be updated in the forthcoming Monthly EM&A Report. |
||||||||
There were no complaints, non-compliance of the WMP, contract-specific WMPs, statutory and contractual requirements that triggered Action and Limit Levels in the reporting period.
Along with the design and construction progress, further development on the treatment level/details and the re-use mode for marine sediment generated from 3RS Project has been conducted according to the EIA recommendation.
5.3
Marine Sediment Management
Marine sediment is managed according to the EIA Report, Updated EM&A Manual and Waste Management Plan of the Project. The sampling process, storage conditions of the excavated marine sediment, treatment process, final backfilling location as well as associated records were inspected and checked by ET and verified by IEC to ensure they were in compliance with the requirements as stipulated in the Waste Management Plan.
Sampling works for marine sediment generated from the reclaimed land area was on-going during the reporting period. The details of the marine sediment sampling, treatment and backfilling will be reported in the subsequent EM&A Reports upon completion.
6
Chinese White Dolphin Monitoring
In accordance with the Manual, CWD monitoring by small vessel line-transect survey supplemented by land-based theodolite tracking survey and passive acoustic monitoring should be conducted during construction phase.
The small vessel line-transect survey should be conducted at a frequency of two full surveys per month, while land-based theodolite tracking survey should be conducted at a frequency of one day per month per station at Sha Chau (SC) and Lung Kwu Chau (LKC) during the construction phase as stipulated in the Manual.
6.1
Action and Limit Levels
The Action and Limit Levels for CWD monitoring were formulated by the action response approach using the running quarterly dolphin encounter rates STG and ANI derived from the baseline monitoring data, as presented in the CWD Baseline Monitoring Report. The derived values of Action and Limit Levels for CWD monitoring were summarised in Table 6.1.
Table 6.1: Derived Values of Action and Limit Levels for Chinese White Dolphin Monitoring
|
|
NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL as a Whole |
|
Action Level(3) |
Running quarterly(1) STG < 1.86 & ANI < 9.35 |
|
Limit Level(3) |
Two consecutive running quarterly(2) (3-month) STG < 1.86 & ANI < 9.35 |
|
Notes: (referring to the baseline monitoring report) (1) Action Level – running quarterly encounter rates STG & ANI of this month will be calculated from the reporting period and the two preceding survey months. (2) Limit Level – two consecutive running quarters mean both the running quarterly encounter rates of the preceding month and the running quarterly encounter rates of this month. (3) Action Level and/or Limit Level will be triggered if both STG and ANI fall below the criteria. |
|
6.2
CWD
Monitoring Transects and Stations
6.2.1
Small Vessel Line-transect Survey
Small vessel line-transect surveys were conducted along the transects covering Northeast Lantau (NEL), Northwest Lantau (NWL), Airport West (AW), West Lantau (WL) and Southwest Lantau (SWL) areas as proposed in the Manual, which are consistent with the Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department (AFCD) long-term monitoring programme (except the addition of AW). The AW transect has not been previously surveyed in the AFCD programme due to the restrictions of HKIA Approach Area, nevertheless, this transect was established during the EIA of the 3RS Project and refined in the Manual with the aim to collect project specific baseline information within the HKIA Approach Area to fill the data gap that was not covered by the AFCD programme. This also provided a larger sample size for estimating the density, abundance and patterns of movements in the broader study area of the project.
The planned vessel survey transect lines following the waypoints set for construction phase monitoring as proposed in the Manual are depicted in Figure 6.1 with the waypoint coordinates of all transect lines given in Table 6.2, which are subject to on-site refinement based on the actual survey conditions and constraints.
Table 6.2: Coordinates of Transect Lines in NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL Survey Areas
|
Waypoint |
Easting |
Northing |
Waypoint |
Easting |
Northing |
|
NEL |
|||||
|
1S |
813525 |
820900 |
6N |
818568 |
824433 |
|
1N |
813525 |
824657 |
7S |
819532 |
821420 |
|
2S |
814556 |
818449 |
7N |
819532 |
824209 |
|
2N |
814559 |
824768 |
8S |
820451 |
822125 |
|
3S |
815542 |
818807 |
8N |
820451 |
823671 |
|
3N |
815542 |
824882 |
9S |
821504 |
822371 |
|
4S |
816506 |
819480 |
9N |
821504 |
823761 |
|
4N |
816506 |
824859 |
10S |
822513 |
823268 |
|
5S |
817537 |
820220 |
10N |
822513 |
824321 |
|
5N |
817537 |
824613 |
11S |
823477 |
823402 |
|
6S |
818568 |
820735 |
11N |
823477 |
824613 |
|
NWL |
|||||
|
1S |
804671 |
814577 |
5S |
808504 |
821735 |
|
1N |
804671 |
831404 |
5N |
808504 |
828602 |
|
2Sb |
805475 |
815457 |
6S |
809490 |
822075 |
|
2Nb |
805476 |
818571 |
6N |
809490 |
825352 |
|
2Sa |
805476 |
820770 |
7S |
810499 |
822323 |
|
2Na |
805476 |
830562 |
7N |
810499 |
824613 |
|
3S |
806464 |
821033 |
8S |
811508 |
821839 |
|
3N |
806464 |
829598 |
8N |
811508 |
824254 |
|
4S |
807518 |
821395 |
9S |
812516 |
821356 |
|
4N |
807518 |
829230 |
9N |
812516 |
824254 |
|
AW |
|||||
|
1W |
804733 |
818205 |
2W |
805045 |
816912 |
|
1E |
806708 |
818017 |
2E |
805960 |
816633 |
|
WL |
|||||
|
1W |
800600 |
805450 |
7W |
800400 |
811450 |
|
1E |
801760 |
805450 |
7E |
802400 |
811450 |
|
2W |
800300 |
806450 |
8W |
800800 |
812450 |
|
2E |
801750 |
806450 |
8E |
802900 |
812450 |
|
3W |
799600 |
807450 |
9W |
801500 |
813550 |
|
3E |
801500 |
807450 |
9E |
803120 |
813550 |
|
4W |
799400 |
808450 |
10W |
801880 |
814500 |
|
4E |
801430 |
808450 |
10E |
803700 |
814500 |
|
5W |
799500 |
809450 |
11W |
802860 |
815500 |
|
5E |
801300 |
809450 |
12S/11E |
803750 |
815500 |
|
6W |
799800 |
810450 |
12N |
803750 |
818500 |
|
6E |
801400 |
810450 |
|
|
|
|
SWL |
|||||
|
1S |
802494 |
803961 |
6S |
807467 |
801137 |
|
1N |
802494 |
806174 |
6N |
807467 |
808458 |
|
2S |
803489 |
803280 |
7S |
808553 |
800329 |
|
2N |
803489 |
806720 |
7N |
808553 |
807377 |
|
3S |
804484 |
802509 |
8S |
809547 |
800338 |
|
3N |
804484 |
807048 |
8N |
809547 |
807396 |
|
4S |
805478 |
802105 |
9S |
810542 |
800423 |
|
4N |
805478 |
807556 |
9N |
810542 |
807462 |
|
5S |
806473 |
801250 |
10S |
811446 |
801335 |
|
5N |
806473 |
808458 |
10N |
811446 |
809436 |
6.2.2
Land-based Theodolite Tracking Survey
Land-based theodolite tracking survey stations were set up at two locations, one facing east/south/west on the southern slopes of Sha Chau (SC), and the other facing north/northeast/northwest at Lung Kwu Chau (LKC). The stations (D and E) are depicted in Figure 6.2 and shown in Table 6.3 with position coordinates, height of station and approximate distance of consistent theodolite tracking capabilities for CWD.
Table 6.3: Land-based Theodolite Survey Station Details
|
Stations |
Location |
Geographical Coordinates |
Station Height (m) |
Approximate Tracking Distance (km) |
|
D |
Sha Chau (SC) |
22° 20’ 43.5” N 113° 53’ 24.66” E |
45.66 |
2 |
|
E |
Lung Kwu Chau (LKC) |
22° 22’ 44.83” N 113° 53’ 0.2” E |
70.40 |
3 |
6.3
CWD
Monitoring Methodology
6.3.1
Small Vessel Line-transect Survey
Small vessel line-transect surveys provided data for density and abundance estimation and other assessments using distance-sampling methodologies, specifically, line-transect methods.
The surveys involved small vessel line-transect data collection and have been designed to be similar to, and consistent with, previous surveys for the AFCD for their long-term monitoring of small cetaceans in Hong Kong. The survey was designed to provide systematic, quantitative measurements of density, abundance and habitat use.
As mentioned in Section 6.2.1, the transects covered NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL areas as proposed in the Manual, which are consistent with the AFCD long-term monitoring programme (except AW). There are two types of transect lines:
● Primary transect lines: the parallel and zigzag transect lines as shown in Figure 6.1; and
● Secondary transect lines: transect lines connecting between the primary transect lines and going around islands.
All data collected on both primary and secondary transect lines were used for analysis of sighting distribution, group size, activities including association with fishing boat, and mother-calf pairs. Only on-effort data collected under conditions of Beaufort 0-3 and visibility of approximately 1200 m or beyond were used for analysis of the CWD encounter rates.
A 15-20m vessel with a flying bridge observation platform about 4 to 5m above water level and unobstructed forward view, and a team of three to four observers were deployed to undertake the surveys. Two observers were on search effort at all times when following the transect lines with a constant speed of 7 to 8 knots (i.e. 13 to 15 km per hour), one using 7X handheld binoculars and the other using unaided eyes and recording data.
During on-effort survey periods, the survey team recorded effort data including time, position (waypoints), weather conditions (Beaufort sea state and visibility) and distance travelled in each series with assistance of a handheld GPS device. The GPS device also continuously and automatically logged data including time, position (latitude and longitude) and vessel speed throughout the entire survey.
When CWDs were seen, the survey team was taken off-effort, the dolphins were approached and photographed for photo-ID information (using a Canon 7D [or similar] camera and long 300 mm+ telephoto lens), then followed until they were lost from view. At that point, the boat returned (off effort) to the survey line at the closest point after obtaining photo records of the dolphin group and began to survey on effort again.
Focal follows of dolphins would be used for providing supplementary information only where practicable (i.e. when individual dolphins or small stable groups of dolphins with at least one member that could be readily identifiable with unaided eyes during observations and weather conditions are favourable). These would involve the boat following (at an appropriate distance to minimise disturbance) an identifiable individual dolphin for an extended period of time, and collecting detailed data on its location, behaviour, response to vessels, and associates.
6.3.2
Photo Identification
CWDs can be identified by their unique features like presence of scratches, nick marks, cuts, wounds, deformities of their dorsal fin and distinguished colouration and spotting patterns.
When CWDs were observed, the survey team was taken off-effort, the dolphins were approached and photographed for photo-ID information (using a Canon 7D [or similar] camera and long 300 mm+ telephoto lens). The survey team attempted to photograph both sides of every single dolphin in the group as the colouration and spotting pattern on both sides may not be identical. The photos were taken at the highest available resolution and stored on Compact Flash memory cards for transferring into a computer.
All photos taken were initially examined to sort out those containing potentially identifiable individuals. These sorted-out images would then be examined in detail and compared to the CWD photo-identification catalogue established for 3RS Project during the baseline monitoring stage.
6.3.3
Land-based Theodolite Tracking Survey
Land-based theodolite tracking survey obtains fine-scale information on the time of day and movement patterns of the CWDs. A digital theodolite (Sokkia/Sokkisha Model DT5 or similar equipment) with 30-power magnification and 5-s precision was used to obtain the vertical and horizontal angle of each dolphin and vessel position. Angles were converted to geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) and data were recorded using Pythagoras software, Version 1.2. This method delivers precise positions of multiple spatially distant targets in a short period of time. The technique is fully non-invasive, and allows for time and cost-effective descriptions of dolphin habitat use patterns at all times of daylight.
Three surveyors (one theodolite operator, one computer operator, and one observer) were involved in each survey. Observers searched for dolphins using unaided eyes and handheld binoculars (7X50). Theodolite tracking sessions were initiated whenever an individual CWD or group of CWDs was located. Where possible, a distinguishable individual was selected, based on colouration, within the group. The focal individual was then continuously tracked via the theodolite, with a position recorded each time the dolphin surfaced. In case an individual could not be positively distinguished from other members, the group was tracked by recording positions based on a central point within the group whenever the CWD surfaced. Tracking continued until animals were lost from view; moved beyond the range of reliable visibility (>1-3km, depending on station height); or environmental conditions obstructed visibility (e.g., intense haze, Beaufort sea state >4, or sunset), at which time the research effort was terminated. In addition to the tracking of CWD, all vessels that moved within 2-3km of the station were tracked, with effort made to obtain at least two positions for each vessel.
Theodolite tracking included focal follows of CWD groups and vessels. Priority was given to tracking individual or groups of CWD. The survey team also attempted to track all vessels moving within 1 km of the focal CWD.
6.4
Monitoring
Results and Observations
6.4.1
Small Vessel Line-transect Survey
Within this reporting period, two complete sets of small vessel line-transect surveys were conducted on the 6, 11, 20, 21, 25, 26, 27 and 28 May 2021, covering all transects in NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL survey areas for twice.
A total of around 450.37 km of survey effort was collected from these surveys and around 83.8% of the survey effort was being conducted under favourable weather condition (i.e. Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility). Details of the survey effort are given in Appendix C.
Sighting Distribution
In May 2021, 12 sightings with 31 dolphins were sighted. Amongst these sightings, 11 sightings with 29 dolphins are on-effort records under favourable weather condition (i.e. Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility). Details of cetacean sightings are presented in Appendix C.
Distribution of all CWD sightings recorded in
May 2021 is illustrated in Figure 6.3. In WL, two CWD sightings were
recorded at Tai O and one sighting was recorded at Peaked Hill. In SWL, the
majority of the CWD sightings were recorded in the western part of the survey
area. No CWD sightings were recorded in neither NEL nor NWL survey areas during
the reporting period.
Figure 6.3: Sightings Distribution of Chinese White Dolphins
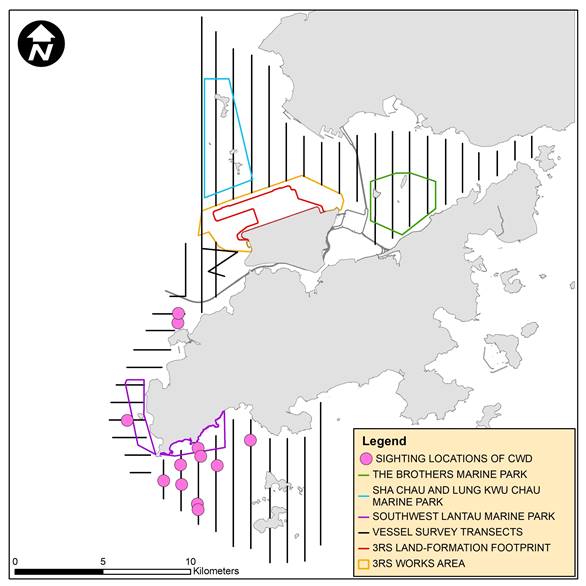
Remarks: (1) Please note that there are 12 pink circles on the map
indicating the sighting locations of CWDs. Some of them were very close to each
other and therefore may appear overlapped on this distribution map. (2) Marine
park excludes land area and the landward boundary generally follows the high
water mark along the coastline.
Encounter Rate
Two types of dolphin encounter rates were calculated based on the vessel survey data. They included the number of dolphin sightings per 100 km survey effort (STG) and total number of dolphins per 100 km survey effort (ANI) in the whole survey area (i.e. NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL). In the calculation of dolphin encounter rates, only survey data collected under favourable weather condition (i.e. Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility) were used. The formulae used for calculation of the encounter rates are shown below:
Encounter Rate by Number of Dolphin Sightings (STG)
![]()
Encounter Rate by Number of Dolphins (ANI)
![]()
(Notes: Only data collected under Beaufort 3 or below condition were used)
In May 2021, a total of around 377.52 km of survey effort were conducted under Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility, whilst a total number of 11 on-effort sightings with 29 dolphins were sighted under such condition. Calculation of the encounter rates for the month are shown in Appendix C.
For the running quarter of the reporting period (i.e., from March to May 2021), a total of around 1130.01 km of survey effort were conducted under Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility, whilst a total number of 26 on-effort sightings and a total number of 70 dolphins from on-effort sightings were obtained under such condition. Calculation of the running quarterly encounter rates are shown in Appendix C.
The STG and ANI of CWD in the whole survey area (i.e. NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL) during the month of May 2021 and during the running quarter are presented in Table 6.4 below and compared with the Action Level. Although the running quarterly encounter rate ANI fall below the Action Level, the Action Level is not triggered as the running quarterly STG remain above the Action Level.
Table 6.4: Comparison of CWD Encounter Rates of the Whole Survey Area with Action Levels
|
|
Encounter Rate (STG) |
Encounter Rate (ANI) |
|
May 2021 |
2.91 |
7.68 |
|
Running Quarter from March to May 2021(1) |
2.30 |
6.19 |
|
Action Level |
Running quarterly(1) STG < 1.86 & ANI < 9.35 |
|
|
Note: (1) Running quarterly encounter rates STG & ANI were calculated from data collected in the reporting period and the two preceding survey months, i.e. the data from March to May 2021, containing six sets of transect surveys for all monitoring areas. Action Level will be triggered if both STG and ANI fall below the criteria. |
||
Group Size
In May 2021, 12 groups of 31 dolphins in total were sighted, and the average group size of CWDs was 2.58 dolphins per group. Sightings with small group size (i.e. 1-2 dolphins) were dominant. There were no CWD sightings with large group size (i.e. 10 or more dolphins).
Activities and Association with Fishing Boats
Two CWD sightings were recorded engaging in feeding activities in May 2021 but no association with operating fishing boats was observed.
Mother-calf Pair
In May 2021, there was one CWD sighting recorded with the presence of mother-and-unspotted juvenile pair of which the sighting was recoded in SWL.
6.4.2
Photo Identification
In May 2021, a total number of 18 different CWD individuals were identified for totally 21 times. A summary of photo identification works is presented in Table 6.5. Representative photos of these individuals are given in Appendix C.
Table 6.5: Summary of Photo Identification
|
Individual ID |
Date of Sighting (dd-mmm-yy) |
Sighting Group No. |
Area |
|
Individual ID |
Date of Sighting (dd-mmm-yy) |
Sighting Group No. |
Area |
|
NLMM061 |
26-May-21 |
2 |
SWL |
|
WLMM004 |
25-May-21 |
7 |
SWL |
|
SLMM003 |
25-May-21 |
6 |
SWL |
|
|
26-May-21 |
3 |
SWL |
|
SLMM010 |
25-May-21 |
4 |
SWL |
|
WLMM007 |
25-May-21 |
4 |
SWL |
|
|
28-May-21 |
2 |
WL |
|
WLMM018 |
25-May-21 |
7 |
SWL |
|
SLMM030 |
25-May-21 |
5 |
SWL |
|
WLMM061 |
11-May-21 |
1 |
WL |
|
SLMM034 |
25-May-21 |
6 |
SWL |
|
WLMM063 |
25-May-21 |
7 |
SWL |
|
SLMM037 |
25-May-21 |
6 |
SWL |
|
|
26-May-21 |
3 |
SWL |
|
SLMM045 |
28-May-21 |
1 |
WL |
|
WLMM065 |
26-May-21 |
2 |
SWL |
|
SLMM049 |
25-May-21 |
4 |
SWL |
|
WLMM079 |
26-May-21 |
3 |
SWL |
|
SLMM052 |
25-May-21 |
6 |
SWL |
|
WLMM135 |
26-May-21 |
3 |
SWL |
|
WLM0027 |
25-May-21 |
3 |
SWL |
|
|
|
|
|
6.4.3
Land-based Theodolite Tracking Survey
Survey Effort
Land-based theodolite tracking surveys were conducted at SC on 13 May 2021 and at LKC on 25 May 2021, with a total of two days of land-based theodolite tracking survey effort accomplished in this reporting period. No CWD groups were tracked during the reporting period. Information of survey effort and CWD groups are presented in Table 6.6. Details of the survey effort are presented in Appendix C.
Table 6.6: Summary of Survey Effort and CWD Group of Land-based Theodolite Tracking
|
Land-based Station |
No. of Survey Sessions |
Survey Effort (hh:mm) |
No. of CWD Groups Sighted |
CWD Group Sighting per Survey Hour |
|
Lung Kwu Chau |
1 |
6:00 |
0 |
0 |
|
Sha Chau |
1 |
6:00 |
0 |
0 |
|
TOTAL |
2 |
12:00 |
0 |
0 |
6.5
Progress Update on Passive Acoustic Monitoring
Underwater acoustic monitoring using Passive Acoustic Monitoring (PAM) should be undertaken during land formation related construction works. During this reporting period, the C-POD was retrieved on 20 May 2021 and the F-POD was deployed and positioned at south of Sha Chau Island inside the SCLKCMP (Figure 6.5). Both C-POD and F-POD are considered as effective PAM devices in detecting CWD occurrence, and F-POD was the main PAM device deployed where feasible. Acoustic data would be reviewed to give an indication of CWDs occurrence patterns and anthropogenic noise information. Analysis would involve use of proprietary software for objective automated data analyses and experienced analysts to perform visual validation for assessment of dolphin detection. As the period of data collection and analysis takes about four months, PAM results could not be reported in monthly intervals but report for supplementing the annual CWD monitoring analysis.
6.6
Site Audit for CWD-related Mitigation Measures
During the reporting period, silt curtains were in place by the contractor for marine filling, in which dolphin observers were deployed by contractor in accordance with the MMWP. Overall, 2 to 5 dolphin observation stations and teams of at least two dolphin observers were deployed by the contractors for continuous monitoring of the DEZ for DCM works and seawall construction works in accordance with the DEZ Plan. Trainings for the proposed dolphin observers on the implementation of MMWP and DEZ monitoring were provided by the ET prior to the aforementioned works, with a cumulative total of 704 individuals being trained and the training records kept by the ET. From the contractors’ MMWP observation records, no dolphin or other marine mammals were observed within or around the silt curtains. As for DEZ monitoring records, no dolphin or other marine mammals were observed within or around the DEZs in this reporting month. These contractors’ records were also audited by the ET during site inspection.
Audits of acoustic decoupling measures for construction vessels were carried out during weekly site inspection and the observations are summarised in Section 7.1. Audits of SkyPier high speed ferries route diversion and speed control and construction vessel management are presented in Section 7.4 and Section 7.5 respectively.
6.7
Timing of
Reporting CWD Monitoring Results
Detailed analysis of CWD monitoring results collected by small vessel line-transect survey will be provided in future quarterly reports. Detailed analysis of CWD monitoring results collected by land-based theodolite tracking survey and PAM will be provided in future annual reports after a larger sample size of data has been collected.
6.8
Summary of CWD Monitoring
Monitoring of CWD was conducted with two complete sets of small vessel line-transect surveys and two days of land-based theodolite tracking survey effort as scheduled. The running quarterly encounter rates STG and ANI in the reporting period did not trigger the Action Level for CWD monitoring.
7
Environmental Site Inspection and Audit
7.1
Environmental Site Inspection
Site inspections of the construction works were carried out on a weekly basis to monitor the implementation of proper environmental pollution control and mitigation measures for the Project. The weekly site inspection schedule of the construction works is provided in Appendix B. Bi-weekly site inspections were also conducted by the IEC. Besides, ad-hoc site inspections were conducted by ET and IEC if environmental problems were identified, or subsequent to receipt of an environmental complaint, or as part of the investigation work. These site inspections provided a direct means to reinforce the specified environmental protection requirements and pollution control measures in construction sites.
During site inspections, environmental situation, status of implementation of pollution control and mitigation measures were observed. Environmental documents and site records, including waste disposal record, maintenance record of environmental equipment, and relevant environmental permit and licences, were also checked on site. Observations were recorded in the site inspection checklist and passed to the contractor together with the recommended mitigation measures where necessary in order to advise contractors on environmental improvement, awareness and on-site enhancement measures. The observations were made with reference to the following information during the site inspections:
· The EIA and EM&A requirements;
· Relevant environmental protection laws, guidelines, and practice notes;
· The EP conditions and other submissions under the EP;
· Monitoring results of EM&A programme;
· Works progress and programme;
· Proposal of individual works;
· Contract specifications on environmental protection; and
· Previous site inspection results.
Good site practices were observed in site inspections during the reporting period. Advice were given when necessary to ensure the construction workforce were familiar with relevant procedures, and to maintain good environmental performance on site. Regular toolbox talks on environmental issues were organised for the construction workforce by the contractors to ensure understanding and proper implementation of environmental protection and pollution control mitigation measures.
A summary of implementation status of the environmental mitigation measures for the construction phase of the Project during the reporting period is provided in Appendix A.
7.2
Landscape and
Visual Mitigation Measures
Implementation of applicable landscape and visual mitigation measures (reference to the environmental protection measures CM1 – CM10 in Appendix A) was monitored in accordance with the Manual. All measures undertaken by both the contractor and the landscape contractor during the construction phase and first year of the operation phase shall be audited by a landscape architect, as a member of the ET, on a regular basis to ensure compliance with the intended aims of the measures. Site inspections shall be undertaken at least once every two months during the operation phase.
The implementation status of the environmental protection measures are summarized below in Table 7.1. Examples of landscape and visual mitigation measures are shown in Table 7.2. The monitoring programme for detailed design, construction, establishment works and long term management (10 years) stages is presented in Table 7.3. Event and Action Plan for Landscape and Visual impacts is stated in Table 7.4.
Table 7.1: Landscape and Visual – Construction Phase Audit Summary
|
Landscape and Visual Mitigation Measures during Construction |
Implementation Status |
Relevant Contract(s) in the Reporting Period |
|
CM1- The construction area and contractor’s temporary works areas shall be minimised to avoid impacts on adjacent landscape. |
The implementation of mitigation measures were checked by ET during weekly site inspection and clarified by the Contractors during the monthly Environmental Management Meetings. Implementation of the measures CM5, CM6 and CM7 by Contractors was observed. |
3RS Project contracts |
|
CM2 – Reduction of construction period to practical minimum |
||
|
CM3 – Phasing of the construction stage to reduce visual impacts during the construction phase. |
||
|
CM4 – Construction traffic (land and sea) including construction plants, construction vessels and barges shall be kept to a practical minimum. |
||
|
CM5 – Erection of decorative mesh screens or construction hoardings around works areas in visually unobtrusive colours. |
||
|
CM6 – Avoidance of excessive height and bulk of site buildings and structures |
||
|
CM7 – Control of night-time lighting by hooding all lights and through minimisation of night working periods |
||
|
CM8 – All existing trees shall be carefully protected during construction. Detailed Tree Protection Specification shall be provided in the Contract Specification. Under this specification, the Contractor shall be required to submit, for approval, a detailed working method statement for the protection of trees prior to undertaking any works adjacent to all retained trees, including trees in contractor’s works areas |
Tree Protection Specifications have been provided in the relevant Contract Specifications respectively for implementation by the Contractors under the Project.
The Contractors’ performance on the implementation of the trees maintenance and protection measures were observed and checked by the ET weekly during construction period. |
3302, 3503, 3508, 3602, 3801
3802 (To be implemented) |
|
CM9 – Trees unavoidably affected by the works shall be transplanted where practical. A detailed Tree Transplanting Specification shall be provided in the Contract Specification, if applicable. Sufficient time for necessary tree root and crown preparation periods shall be allowed in the project programme |
Tree Transplanting Specifications have been provided in the relevant Contract Specifications respectively for implementation by the Contractors under the Project where trees will unavoidably be affected by the construction works.
The Contractors were required to submit Method Statements for tree transplanting prior to the transplanting works. Tree inspections were conducted by ET to check the tree transplanting works implemented by the Contractors on site.
The Contractors’ performance on the implementation of trees maintenance and protection measures on transplanted trees were observed and checked by the ET bi-monthly during the 12-month establishment period after the completion of each batch of transplanting works.
Long term management of the transplanted trees were currently monitored by ET annually. |
3503, 3508, 3801
3802 (To be implemented) |
|
CM 10 – Land formation works shall be followed with advanced hydroseeding around taxiways and runways as soon as practical |
To be implemented around taxiways and runways as soon as practicable. |
To be implemented |
Table 7.2: Examples of Landscape and Visual Mitigation Measures in the Reporting Period
|
|
|
|
|
Erection of site hoardings around works area in unobtrusive colours (CM5) |
Avoidance of excessive height and bulk of site buildings (CM6) |
Control of night-time lighting by hooding and minimisation of night working period (CM7) |
|
|
|
|
|
General view of Tree Protection Zone for retained tree (CM8) |
General view of a transplanted tree (CM9) |
|
In accordance with the EM&A Manual, all existing trees shall be protected carefully during construction. Trees unavoidably affected by the works shall be transplanted where practical. In this reporting period, the cumulative total number of retained and transplanted trees under the Project were 98 and 14, respectively. A works area including 4 retained trees was handed over from Contract 3801 to Contract 3508 during the reporting period. Moreover, Contract 3801 has reviewed their initial tree survey areas and confirmed that some of the surveyed areas were not to be their works areas and therefore 41 retained trees were excluded from the Project. One retained tree was removed due to safety concern of Airport Express Line (AEL) operation. Details of the retained trees, transplanted trees and to-be-transplanted trees under the Project are summarized in Table 7.5. Photos of transplanted trees are presented in Table 7.7.
Details of the retained trees are to be discussed in the Quarterly EM&A reports.
Table 7.3: Monitoring Programme for Landscape and Visual
|
Stage |
Monitoring Task |
Monitoring Report |
Form of Approval |
Frequency |
|
Detailed Design |
Checking of design works against the recommendations of the landscape and visual impact assessments within the EIA shall be undertaken during detailed design and tender stage, to ensure that they fulfil the intention of the mitigation measures. Any changes to the design, including design changes on site shall also be checked. |
Report by AAHK / PM confirming that the design conforms to requirements of EP. |
Approved by Client
|
At the end of the Detailed Design Phase |
|
Construction |
Checking of the contractor’s operations during the construction period. |
Report on Contractor's compliance, by ET |
Counter signature of report by IEC |
Weekly |
|
Establishment Works |
Checking of the planting works during the twelve-month Establishment Period after completion of each batch of transplanting works. |
Report on Contractor's compliance, by ET |
Counter signature of report by IEC |
Every two months |
|
Long Term Management (10 year) |
Monitoring of the long-term management of the planting works in the period up to 10 years after completion of each batch of transplanting works. |
Report on Compliance by ET or Maintenance Agency as appropriate |
Counter signature of report by Management Agency |
Annually |
Table 7.4: Event and Action Plan for Landscape and Visual
|
Event Action Level |
Action |
|||
|
|
ET |
IEC |
AAHK / PM |
Contractor |
|
Design Check |
Check final design conforms to the requirements of EP and prepare report. |
Check report. Recommend remedial design if necessary. |
Undertake remedial design if necessary. |
|
|
Non-conformity on one occasion |
Identify source. Inform IEC and AAHK / PM. Discuss remedial actions with IEC, AAHK / PM and Contractor. Monitor remedial actions until rectification has been completed. |
Check report. Check Contractor’s working method. Discuss with ET and Contractor on possible remedial measures. Advise AAHK / PM on effectiveness of proposed remedial measures. Check implementation of remedial measures. |
Notify Contractor. Ensure remedial measures are properly implemented. |
Amend working methods to prevent recurrence of non-conformity. Rectify damage and undertake additional action necessary. |
|
Repeated Non-conformity |
Identify source. Inform IEC and AAHK / PM. Increase monitoring frequency. Discuss remedial actions with IEC, AAHK / PM and Contractor. Monitor remedial actions until rectification has been completed. If non-conformity stops, cease additional monitoring. |
Check monitoring report. Check Contractor’s working method. Discuss with ET and Contractor on possible remedial measures. Advise AAHK / PM on effectiveness of proposed remedial measures. Supervise implementation of remedial measures. |
Notify Contractor. Ensure remedial measures area properly implemented. |
Amend working methods to prevent recurrence of non-conformity. Rectify damage and undertake additional action necessary. |
Table 7.5: Summary of the Number of Retained, Transplanted and To-be-transplanted Trees in the Reporting Period
|
Existing |
|
|
|
|
|
Contract |
Retain (nos.) |
Transplanted (nos.) |
To-be-transplanted (nos.) |
|
|
Establishment Period |
Maintenance Period |
|||
|
3302 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
3503 |
19 |
6 |
3 |
0 |
|
3508(1) |
25 |
0 |
0 |
12 |
|
3602 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
3801 |
43 |
0 |
5 |
0 |
|
Sub-total |
98 |
6 |
8 |
12 |
|
Provisional |
|
|
|
|
|
Contract |
Retain (nos.) |
Transplanted (nos.) |
To-be-transplanted (nos.) |
|
|
3508(1) |
130 |
0 |
10 |
|
|
Sub-total |
130 |
0 |
10 |
|
|
Grand Total |
228 |
14 |
22 |
|
(1) As some of the site areas have been handed over to Contract 3508, Contractor of Contract 3508 is currently managing some of the trees. Existing trees to be managed by Contract 3508 is subject to change after initial tree surveys for each batch of site areas have been conducted by the Contractor.
Summary of the updated transplanted trees and photos are presented in Table 7.6 and Table 7.7 respectively.
Table 7.6: Summary of the Transplanted Trees Updated in the Reporting Period
|
Tree ID |
Transplant Date |
Management Stage |
Management Agency |
Remarks |
|
CT276
|
3 May 2018
|
Establishment period 4 May 2018 – May 2019 |
Contract 3801 |
Next inspection will be conducted in February 2022. Photos of the last inspection in February 2021 can be referred to Table 7.7 of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.62. |
|
Long Term Management period Jun 2019 – May 2028 |
Southern Landside Petrol Filling Station |
|||
|
CT1253
|
4 May 2018
|
Establishment period 5 May 2018 – May 2019 |
Contract 3801 |
|
|
Long Term Management period Jun 2019 – May 2028 |
Southern Landside Petrol Filling Station |
|||
|
T835 |
22 Jan 2020 |
Establishment period 23 Jan 2020 – Jan 2021 |
Contract 3503
|
Next inspection will be conducted in February 2022. Photos of the last inspection in February 2021 can be referred to Table 7.7 of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.62. |
|
Long Term Management period Feb 2021 – Jan 2030 |
||||
|
T836 |
13 Dec 2019 |
Establishment period 14 Dec 2020 – Jan 2021 |
Contract 3503
|
|
|
Long Term Management period Feb 2021 – Jan 2030 |
||||
|
T838 |
22 Jan 2020 |
Establishment period 23 Jan 2020 – Jan 2021 |
Contract 3503
|
|
|
Long Term Management period Feb 2021 – Jan 2030 |
||||
|
T812 |
21 Dec 2020 |
Establishment period 22 Dec 2020 – Dec 2021 |
Contract 3503 |
Next inspection will be conducted in June 2021. Photos of the last inspection in May 2021 were shown in Table 7.7.
|
|
T814 |
20 Dec 2020 |
Establishment period 21 Dec 2020 – Dec 2021 |
Contract 3503 |
|
|
T815 |
15 Dec 2020 |
Establishment period 16 Dec 2020 – Dec 2021 |
Contract 3503 |
|
|
T829 |
18 Dec 2020 |
Establishment period 19 Dec 2020 – Dec 2021 |
Contract 3503 |
|
|
T830 |
14 Dec 2020 |
Establishment period 15 Dec 2020 – Dec 2021 |
Contract 3503 |
|
|
T831 |
19 Dec 2020 |
Establishment period 20 Dec 2020 – Dec 2021 |
Contract 3503 |
|
|
CT1194 |
4 May 2018 |
Establishment period 5 May 2018 – May 2019 |
Contract 3801 |
NA |
|
Long Term Management period Jun 2019 – May 2028 |
Southern Landside Petrol Filling Station |
Uprooted and collapsed due to Typhoon Higos on 18 August 2020. Tree removal was conducted as recommended by tree specialist of the contractor of Southern Landside Petrol Filing Station. |
||
|
CT1794 |
3 May 2018 |
Establishment period 4 May 2018 – May 2019 |
Contract 3801 |
NA |
|
Long Term Management period Jun 2019 – May 2028 |
AsiaWorld-Expo |
The tree within the land parcel was acquired by the government for construction of emergency hospital to handle COVID19 pandemic at AsiaWorld-Expo. The tree was felled in late 2020. |
||
|
CT1795 |
3 May 2018 |
Establishment period 4 May 2018 – May 2019 |
Contract 3801 |
NA |
|
Long Term Management period Jun 2019 – May 2028 |
AsiaWorld-Expo |
The tree within the land parcel was acquired by the government for construction of emergency hospital to handle COVID19 pandemic at AsiaWorld-Expo. The tree was felled in late 2020. |
Table 7.7: Photos of the Existing Transplanted Trees
|
Under 12-month Establishment Period: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
T812 |
T814 |
T815 |
|
|
|
|
|
T829 |
T830 |
T831 |
7.3 Land Contamination Assessment
The Supplementary CAP was submitted to EPD pursuant to EP Condition 2.20. The CARs for Golf Course and T2 Emergency Power Supply Systems (EPSS) were submitted to EPD in accordance with EP Condition 1.9 and the Supplementary CAP in which no land contamination issues were identified. EPD has issued no further comment for aforesaid CARs. No leakage was found after the removal of underground fuel pipelines and all required additional photos have been submitted to EPD.
According to the approved supplementary CAP, there are 3 remaining locations where site re-appraisal / additional site investigation are proposed. Based on the latest construction information, which has been presented in Appendix A Implementation Schedule of the approved CARs for T2 EPSS, there is no development programme for these locations at this stage. As such, the status of site re-appraisal/ additional site investigation shall be further updated upon latest development programme is available.
7.4
Audit of SkyPier High Speed
Ferries
The Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for High Speed Ferries of SkyPier (the SkyPier Plan) was submitted to the Advisory Council on the Environment for comment and subsequently submitted to and approved by EPD in November 2015 under EP Condition 2.10. The approved SkyPier Plan is available on the dedicated website of the Project. In the SkyPier Plan, AAHK has committed to implement the mitigation measure of requiring HSFs of SkyPier travelling between HKIA and Zhuhai / Macau to start diverting the route with associated speed control across the area, i.e. Speed Control Zone (SCZ), with high CWD abundance. The route diversion and speed restriction at the SCZ have been implemented since 28 December 2015.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, all SkyPier HSF services to/from Zhuhai and Macau have been suspended from 25 March 2020 until further notice. No ferry movement between HKIA SkyPier and Zhuhai and Macau was recorded in May 2021. Key audit findings for the SkyPier HSFs travelling to/from Zhuhai and Macau against the requirements of the SkyPier Plan during the reporting period are summarised in Table 7.8.
The daily movement of all SkyPier HSFs, including those not using the diverted route, in this reporting period (i.e., 2 to 3 daily movements) were within the maximum daily cap of 125 daily movements. Status of compliance with the annual daily average of 99 movements will be further reviewed in the Annual EM&A Report.
As updated by CLP Power, the construction works of the Hong Kong Offshore LNG Terminal Project may affect the route diversion operation of the SkyPier HSFs from Q3 to Q4 2021. The captains were informed on the issue and ET will continue to closely monitor the implementation of the SkyPier Plan in the period.
Table 7.8: Summary of Key Audit Findings against the SkyPier Plan
|
Requirements in the SkyPier Plan |
1 to 31 May 2021 |
|
Total number of ferry movements recorded and audited for HSF to/from Zhuhai and Macau |
0 |
|
Use diverted route and enter / leave SCZ through Gate Access Points |
0 deviation |
|
Daily Cap for all SkyPier HSFs including those not using diverted route
|
2 to 3 daily movement (within the maximum daily cap - 125 daily movements) |
7.5
Audit of
Construction and Associated Vessels
ET carried out the following actions during the reporting period:
- Two skipper training sessions were held for
contractors’ concerned skippers of relevant construction vessels to
familiarize them with the predefined routes; general education on local
cetaceans; guidelines for avoiding adverse water quality impact; the
required environmental practices / measures while operating construction
and associated vessels under the Project; and guidelines for operating
vessels safely in the presence of CWDs. The list of all trained skippers
was properly recorded and maintained by ET.
- Five skipper training sessions were held by
contractors’ Environmental Officers. Competency tests were subsequently
conducted with the trained skippers by ET. The list of all trained
skippers was properly recorded and maintained by ET.
- Based on the updated record, 8 skippers were trained by
ET and 15 skippers were trained by contractors’ Environmental Officers in
the previous period. In this reporting period, 30 skippers were trained by
ET and 7 skippers were trained by contractors’ Environmental Officers. In
total, 1784 skippers were trained from August 2016 to May 2021.
- The
MSS automatically recorded deviation cases such as speeding, entering no
entry zone and not travelling through the designated gate. ET conducted
checking to ensure the MSS records deviation cases accurately.
· Deviations such as speeding in the works area, entered no entry zone, and entering from non-designated gates were identified. All the concerned contractors were reminded to comply with the requirements of the MTRMP-CAV during the bi-weekly Construction Traffic Control Centre (CTCC) audit.
- Three-month
rolling programmes (one month record and three months forecast) for construction
vessel activities were received from the contractors in order to help
maintain the number of construction and associated vessels on site to a
practicable minimal level.
7.6
Implementation
of Dolphin Exclusion Zone
During the reporting period, ET was notified that no dolphin sightings were recorded within the DEZ by the contractors. The ET checked the dolphin sighting record and relevant records by the contractors to audit the implementation of DEZ.
7.7
Status of
Submissions under Environmental Permits
The current status of submissions under the EP up to the reporting period is presented in Table 7.9.
Table 7.9: Status of Submissions under Environmental Permit
|
EP Condition |
Submission |
Status |
|
2.1 |
Complaint Management Plan |
Accepted / approved by EPD
|
|
2.4 |
Management Organizations |
|
|
2.5 |
Construction Works Schedule and Location Plans |
|
|
2.7 |
Marine Park Proposal |
|
|
2.8 |
Marine Ecology Conservation Plan |
|
|
2.9 |
Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for Construction and Associated Vessels |
|
|
2.10 |
Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for High Speed Ferries of SkyPier |
|
|
2.11 |
Marine Mammal Watching Plan |
|
|
2.12 |
Coral Translocation Plan |
|
|
2.13 |
Fisheries Management Plan |
|
|
2.14 |
Egretry Survey Plan |
|
|
2.15 |
Silt Curtain Deployment Plan |
|
|
2.16 |
Spill Response Plan |
|
|
2.17 |
Detailed Plan on Deep Cement Mixing |
|
|
2.18 |
Landscape & Visual Plan |
|
|
2.19 |
Waste Management Plan |
|
|
2.20 |
Supplementary Contamination Assessment Plan |
|
|
3.1 |
Updated EM&A Manual |
|
|
3.4 |
Baseline Monitoring Reports |
7.8
Compliance with
Other Statutory Environmental Requirements
During the reporting period, environmental related licenses and permits required for the construction activities were checked. No non-compliance with environmental statutory requirements was recorded. The environmental licenses and permits which are valid in the reporting period are presented in Appendix E.
7.9
Analysis and
Interpretation of Complaints, Notification of Summons and Status of
Prosecutions
7.9.1
Complaints
Complaint received in the previous reporting period
For the complaint received on 20 April 2021 regarding alleged dusty and muddy vehicles from 3RS Project at Tuen Mun Public Cargo Working Area (TMPCWA), the case was investigated by ET in accordance with the Manual and the Complaint Management Plan of the Project. The ET requested the related 3RS contractors to provide more information regarding the complaint. According to the information provided by the contractors, the ET identified the relevant contractor and noted the alleged vehicle was a cement truck transported by RoRo barge service running between the 3RS reclaimed land and TMPCWA. Based on ET’s regular site inspections on this contract in April 2021, it was observed that the contractor had conducted wheel washing on vehicles prior to leaving the works area.
An ad hoc inspection at TMPCWA was arranged after receiving the complaint. While no RoRo barge was observed at TMPCWA during the inspection, soil and sand were observed on the road surface. Another ad hoc inspection at North Eastern Quay on 3RS reclaimed land, the location of the said RoRo barge service, was conducted in early May 2021 where dusty surfaces at the quay area was observed. The ET reminded the quay-managing contractor to provide adequate water spraying at the quay area. Having said that, it was noted that all air quality monitoring results of the Project in April 2021 were within the corresponding Action and Limit Levels at all monitoring stations.
To follow up, individual contractors were reminded to properly wash the wheels of outgoing trucks from their respective construction sites. In the short term, a section of haul road connected to the quay would be paved to reduce fugitive dust generation and manual wheel washing would be implemented continuously. In the long term, an enhanced wheel washing measure is planned at both the North Eastern and Western Quay on the 3RS reclaimed land. ET and IEC would continue to monitor the wheel washing performance of all the contractors during the environmental site inspections. The complaint case was considered closed.
Complaint received in this reporting period
For the complaint received on 14 May 2021 regarding dust issue at 3RS construction site area, the case was investigated by ET in accordance with the Manual and the Complaint Management Plan of the Project. The anonymous complainant provided photos and did not provide any details on the complaint such as time and location of the observation. The ET recognized the concerned area and identified one related 3RS contractor and requested the contractor to provide information regarding the complaint. The contractor replied they had enhanced dust suppression measures by installing 360-degree water sprinklers. They also provided water spraying record of May and their dust control management plan. After receiving the complaint, a joint inspection by ET, IEC and AAHK was arranged, in which sprinklers and water trucks were both observed operating, and the installation of more sprinklers was underway at the concerned area. Nonetheless, ET reminded the contractor to enhance dust mitigation measures at the concerned area and review the dust control management plan regularly. Proper dust mitigation measures were observed during another joint inspection by ET, AAHK and EPD in late May 2021. In parallel, ET checked the daytime wind speed for 12 May 2021 at Chek Lap Kok wind station of Hong Kong Observatory. It was noted that the wind speed reached 26-27km/hr for several periods of time which might suggest the presence of sudden gust at the concerned area. Moreover, all air quality monitoring results of the Project in May 2021 were within the corresponding Action and Limit Levels at all monitoring stations. In view of the information mentioned above, the dust generation might be caused by sudden gust. Having said that, ET reminded the contractor to regularly review and update their dust control management plan and continue implementing dust mitigation measures according to the plan. ET and IEC would continue to monitor the related contractor’s dust mitigation measures during the environmental site inspections. Hence, the complaint case was considered closed.
7.9.2 Notifications of Summons or
Status of Prosecution
Neither notification of summons nor prosecution was received during the reporting period.
7.9.3
Cumulative
Statistics
Cumulative statistics on complaints, notifications of summons and status of prosecutions are summarised in Appendix F.
8 Future Key Issues and Other EIA & EM&A Issues
8.1
Construction Programme for the Coming Reporting Period
Key activities anticipated in the next reporting period for the Project will include the following:
Contract 3206 Main Reclamation Works
● DCM works;
● Land-based ground improvement works;
● Seawall construction;
● Marine filling; and
● Sorting and reuse of inert waste from other 3RS contracts.
Airfield Works:
Contract 3301 North Runway Crossover Taxiway
● Cable ducting works; and
● Paving works.
Contract 3302 Eastern Vehicular Tunnel Advance Works
● Cable laying and ducting works;
● Backfilling and reinstatement works; and
● Piling and structure works;
Contract 3303 Third Runway and Associated Works
● Land-based ground improvement works;
● Operation of asphalt plant;
● Footing and utilities work; and
● Cable laying and ducting works.
Contract 3305 Airfield Ground Lighting System
● Genset installation; and
● Site establishment.
Contract 3307 Fire Training Facility
● Architectural, Builder's and Finishing works;
● Drainage and utilities works; and
● Building construction.
Third Runway Concourse:
Contract 3403 New Integrated Airport Centres Building and Civil Works
● Architectural, Builder's Work and Finishing works;
● Underground utilities construction;
● Footing construction; and
● Pre-boring and sheetpiling works.
Contract 3405 Third Runway Concourse Foundation and Substructure Works
● Foundation works;
● Piling work;
● Excavation and backfilling; and
● Road formation.
Terminal 2 Expansion:
Contract 3503 Terminal 2 Foundation and Substructure Works
● T2 re-configuration;
● Excavation works;
● Utilities and road work; and
● Piling and structure works.
Contract 3508 Terminal 2 Expansion Works
● Excavation and footing construction;
● Site formation;
● Piling work; and
● Builders’ works.
Automated People Mover (APM) and Baggage Handling System (BHS):
Contract 3601 New Automated People Mover System (TRC Line)
● Rebar fixing;
● Formwork erection and removal;
● Guidebeam installation; and
● Concreting work.
Contract 3602 Existing APM System Modification Works
● Car modification; and
● Concreting work.
Construction Support (Facilities):
Contract 3721 Construction Support Infrastructure Works
● Excavation and backfilling;
● Laying of drainage pipes and ducts; and
● Road works.
Contract 3722 Construction Support Facilities
● Foundation works;
● Erection of superstructure; and
● Site establishment.
Contract 3723 Construction Support Facilities
● Foundation works;
● Erection of superstructure; and
● Site establishment.
Airport Support Infrastructure:
Contract 3801 APM and BHS Tunnels on Existing Airport Island
● Formwork and rebar fixing;
● Construction of working platform;
● Cofferdam for shaft;
● Site clearance; and
● Demolition works.
Contract 3802 APM and BHS Tunnels and Related Works
● Construction of Airside Fire Station and marine sediment treatment plant;
● Installation of sheet pipes and dewatering well;
● Pre-drilling; and
● Ducting works.
Construction Support (Services / Licenses):
Contract 3901A Concrete Batching Facility
● Plant operation; and
● Material conveyor belt construction.
Contract 3901B Concrete Batching Facility
● Plant operation; and
● Foundation works for conveyor belt.
8.2
Key Environmental Issues for the Coming Reporting Period
The key environmental issues for the Project in the coming reporting period expected to be associated with the construction activities include:
● Generation of dust from construction works and stockpiles;
● Noise from operating equipment and machinery on-site;
● Generation of site surface runoffs and wastewater from activities on-site;
● Water quality from DCM works and marine filling;
● DEZ monitoring for ground improvement works (DCM works) and seawall construction;
● Implementation of MMWP for silt curtain deployment;
● Sorting, recycling, storage and disposal of general refuse and construction waste;
● Reuse of treated marine sediments from piling and excavation works;
● Management of chemicals and avoidance of oil spillage on-site; and
● Acoustic decoupling measures for equipment on marine vessels.
The implementation of required mitigation measures by the contractors will be monitored by the ET.
8.3
Monitoring
Schedule for the Coming Reporting Period
A tentative schedule of the planned environmental monitoring work in the next reporting period is provided in Appendix B.
8.4
Review of the Key Assumptions Adopted in the EIA Report
With reference to Appendix E of the Manual, it is noted that the key assumptions adopted in approved EIA report for the construction phase are still valid and no major changes are involved. The environmental mitigation measures recommended in the approved EIA Report remain applicable and shall be implemented in undertaking construction works for the Project.
9 Conclusion and Recommendation
The key activities of the Project carried out in the reporting period included reclamation works and land-based works. Works in the reclamation areas included DCM works, marine filling, seawall and facilities construction, together with runway and associated works. Land-based works on existing airport island involved mainly airfield works, foundation and substructure work for Terminal 2 expansion, modification and tunnel work for APM and BHS systems, and preparation work for utilities, with activities include site establishment, site office construction, road and drainage works, cable ducting, demolition of existing facilities, piling, and excavation works.
All the monitoring works for construction dust, construction noise, water quality, construction waste, landscape & visual, and CWD were conducted during the reporting period in accordance with the Manual.
Monitoring results of construction dust, construction noise, water quality, construction waste, and CWD did not trigger the corresponding Action and Limit Levels during the reporting period.
One monitoring result of construction noise exceeded the relevant Limit Level, and the corresponding investigation was conducted as stipulated in the EM&A programme. The investigation findings concluded that the exceedance was not due to the Project.
The water quality monitoring results for all parameters, except suspended solids (SS), obtained during the reporting period were within the corresponding Action and Limit Levels stipulated in the EM&A programme. Relevant investigation and follow-up actions will be conducted according to the EM&A programme if the corresponding Action and Limit Levels are triggered. For SS, one of the testing results triggered the relevant Action Level, and the corresponding investigation was conducted accordingly. The investigation findings concluded that the case was not related to the Project. To conclude, the construction activities in the reporting period did not introduce adverse impact to all water quality sensitive receivers.
Weekly site inspections of the construction works were carried out by the ET to audit the implementation of proper environmental pollution control and mitigation measures for the Project. Bi-weekly site inspections were also conducted by the IEC. Site inspection findings were recorded in the site inspection checklists and provided to the contractors to follow up.
On the implementation of the SkyPier Plan, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, all SkyPier HSF services to/from Zhuhai and Macau have been suspended from 25 March 2020 until further notice. No HSF movement between HKIA SkyPier and Zhuhai and Macau was recorded during the reporting period. Therefore, no deviation was recorded in the HSF monitoring in the reporting period. The daily movements of all SkyPier HSFs in the reporting period, including those not using the diverted route, were in the range of 2 to 3 daily movements, which are within the maximum daily cap of 125 daily movements.
On the implementation of MTRMP-CAV, the MSS automatically recorded the deviation case such as speeding, entering no entry zone and not travelling through the designated gates. ET conducted checking to ensure the MSS records all deviation cases accurately. Training has been provided for the concerned skippers to facilitate them in familiarising with the requirements of the MTRMP-CAV. Deviations including speeding in the works area, entered no entry zone, and entry from non-designated gates were reviewed by ET. All the concerned captains were reminded by the contractor’s CTCC representative to comply with the requirements of the MTRMP-CAV. The ET reminded contractors that all vessels shall avoid entering the no-entry zone, in particular the Brothers Marine Park and the Sha Chau & Lung Kwu Chau Marine Park. Three-month rolling programmes for construction vessel activities, which ensures the proposed vessels are necessary and minimal through good planning, were also received from contractors.
[1] The Manual is available on the Project’s dedicated website (accessible at: http://env.threerunwaysystem.com/en/index.html).













